Actuarial Practice Standard (27) Employee Benefits issued by Institute of Actuaries of India
Financial reporting in India underwent a transformation owing to the adoption of Indian Accounting Standards (Ind AS) that are converged with IFRSs. Now, the Institute of Actuaries of India has introduced a new Actuarial Practice Standard (APS) on Employee Benefits (APS 27) (the “Standardâ€), which applies to all actuarial work relating to employee benefits (including valuations carried out for accounting and reporting purposes). The new Standard seeks to enhance / strengthen reporting requirements on practitioners whilst providing them with a principle based set of standards to ensure that the user / recipient of actuarial work is able to place a high degree of reliance on the same.
You can access the new APS by clicking on any of the following links:
http://www.kpac.co.in/images/APS-27-Employee-Benefits.pdf
http://www.actuariesindia.org/downloads/APS/APS%2027%20-%20Employee%20Benefits.pdf
The purpose of this article is to provide a high level overview of APS 27, including its key requirements.
Introduction of APS 27 and Replacement of Existing Standards
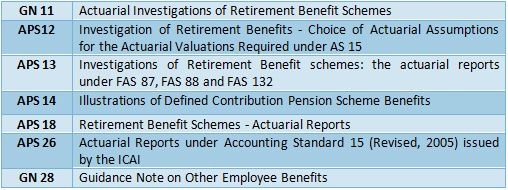
APS 27 is a Practice Standard i.e., mandatory and has become effective from 1st January 2018. As a result of the introduction of APS 27, following existing Actuarial Practice Standards / Guidance Notes issued by the Institute of Actuaries of India in the past stand simultaneously withdrawn:
Purpose of APS 27
APS 27 aims to provide a principle based set of standards that apply to all actuarial work relating to employee benefits. It seeks to ensure that the user of actuarial work is able to place a high degree of reliance on the output of actuarial work relating to employee benefits.
The framework of APS 27 is not meant to be technically prescriptive and does not interpret any legislation or rule or Accounting Standard. However, there is a “Technical Application Section†in the Standard that outlines how some of the principles should be applied in the Indian context, given the nuances of the most prevalent type of employee benefit plans with which the members are involved.
Thus, the core text of the Standard is divided into two key parts viz. the “GENERAL PRINCIPLES†and the “TECHNICAL APPLICATION SECTIONâ€.
GENERAL PRINCIPLES contained in APS 27
The Standard lays down general principles that must be adhered to when performing an actuarial work relating to employee benefits, including laying down general reporting requirements relating to the actuarial work performed. Some of the key reporting requirements of the Standard, in relation to the routine employee benefit valuations (i.e. gratuity valuation, pension valuation, leaves valuation, etc) are as follows:
- The member must ensure that his/her role in a particular assignment is clear and understood by the user. The member must state the capacity in which he/she is providing actuarial advice, the scope, its purpose, and for whom the actuarial work has been performed.
- The member must clearly state the extent to which any third party can rely on the actuarial work performed and its limitations for use by third parties. Such third parties may include a company’s statutory auditor or legal adviser.
- If there is any uncertainty, for instance, impact of legislation on the calculation of benefits, the member’s report should include necessary references to the same.
- The member may place reliance on information received from a third party as an input to perform actuarial work. The information relied upon, its source and the extent of the checks applied by the member in order to the accuracy and relevance of the information must be disclosed in the report.
- In case the assumptions are not determined by the member but received as an input for the valuation and the member has relied on the same or has not validated the appropriateness or adequacy of the assumptions, the same must be clearly spelt out in his/her report along with his views on general appropriateness of the assumptions.
- The member must include statement of benefits which have been valued and highlighting any changes since the most recent similar investigation.
- The member must include a brief summary of the data on which the investigation is based, including but not limited to the number of employees, total wages/salaries, etc in his / her report. The report provided should state that the member is satisfied with the accuracy and sufficiency of the data. In case of any reservation as to the reliability of the data, appropriate qualification should be made therein.

- When describing the method and assumptions used, the report should highlight the factors that the results will be most sensitive to, and where appropriate, also indicate the quantum of this sensitivity through scenarios.
Requirements of TECHNICAL APPLICATION SECTION (TAS) of APS 27
In addition to the general principles, the Technical Application Section (Section 9 of the Standard) lists down certain specific considerations / reporting requirements for the following types of routine actuarial valuations carried out for accounting and reporting purposes:
- Actuarial valuation of gratuity benefit i.e. gratuity valuation
- Actuarial valuation of leave (Privilege / Earned, Sick etc.) benefit i.e. leave valuation
- Actuarial valuation of pension benefit i.e. pension valuation
- Actuarial valuation of post-retirement medical benefit scheme
- Actuarial valuation of long service awards (other employee benefits)
For each of the above, the Technical Application Section lays down certain aspects relating to the following elements of actuarial work, which must be considered and demonstrated (i.e. reported) in an actuarial valuation report:
- Data: The Section specifies the items relating to data which should be reported in an actuarial valuation report, which typically includes number of employees, past service, salary used, leave balance (in case of leave valuation), average age, etc. In case of pensions / PRMS valuation, the Section requires that separate summary statistics of data be included for each beneficiary type i.e. current employees, retirees, spouse of retirees in case of death of the employee etc.
- Assumptions: The Section requires that a valuation report should give details of all the assumptions used in the valuation, which typically includes salary growth rate (including pensions growth rate), discount rate, attrition rate, mortality / disability rate, leave availment and encashment rate (in case of leave valuation), etc. In case of pensions / PRMS valuation, the Section requires that a description be provided of how mortality improvements that may have happened since the publication of mortality tables have been considered in the valuation.
- Modeling / Model: The Section requires that the valuation report should include complete description of the required benefits valued.
- Report / Output: The Section requires that the member should ensure application of the Projected Unit Credit (PUC) Method in attributing benefit to the service rendered in the past and that his / her report shall clearly and completely spell out all the inputs (data, assumptions and benefit structure) considered for valuation and that the report should include disclosures and disclaimers on the extent each of the inputs have been validated.
Further details on the requirements of the Technical Application Section for each type of actuarial valuation shall follow in our subsequent write ups / articles.
Concluding Thoughts
In our view, the introduction of APS 27 is going to enhance quality of reporting carried out by practitioners working in the area of employee benefits. Not only will this improve understandability of actuarial reports by non-practitioners, it will also enable the management and auditors to make better decisions about the choice of assumptions. Enhanced reporting requirements will also enable better understanding of these liabilities, which may pave the way for better management of these (usually ‘long-term’ and ‘real’) liabilities.
I thank you for reading this note and welcome any comments or recommendations or observations you may have on the subject. You can direct those to the email address mentioned below.

Khushwant Pahwa, FIAI, FIA, B Com (H)
Founder and Consulting Actuary
KPAC (Actuaries and Consultants)
k.pahwa@kpac.co.in
www.kpac.co.in

